Predicting Helpful Posts
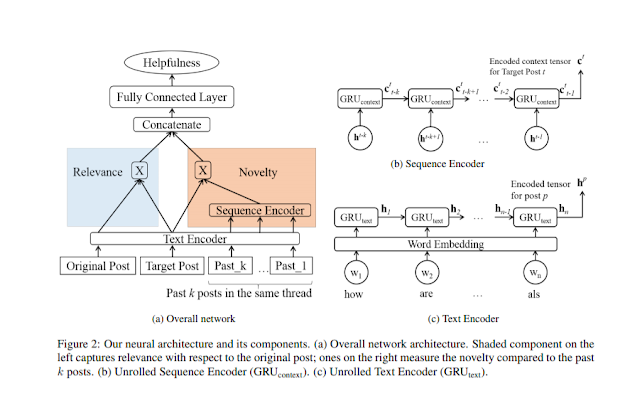
Original paper: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/N19-1318 Here is a quick summary: The research purpose is to identify helpful posts from discussion threads in forums, especially long-running discussions. The approach is to model the relevance of each post concerning the original post and the novelty (not presented in the earlier posts of the discussion thread)of a post based on a windowed context. To model, the 'relevance' the original post and the target post are encoded using an RNN (GRU). The encoded sequences are then element-wise multiplied. As for modeling of the 'novelty,' the target post and the past K posts (where K is the number of past posts taken into context. A 'K' between 11 to 7 worked best for the Reddit dataset used in the experiment - performance stops improving after a certain number of posts taken into context) are also encoded using the same RNN text encoder. Once the 'K' posts are text encoded it is then fed thru another R...